-
About
- Kyoto Prize
-
Research Grants
-
News
This website uses cookies to improve the user experience. If you continue on this website, you will provide your consent to our use of cookies.
About
Research Grants
News

Assistant Professor, Research Institute of Environmental Medicine, Nagoya University *Profile is at the time of the award.
2021Inamori Research GrantsBiology & Life sciences
By clarifying the crosstalk mechanism between lipid metabolism and immune response, we aim to propose new dietary strategies to prevent or treat autoimmune diseases.
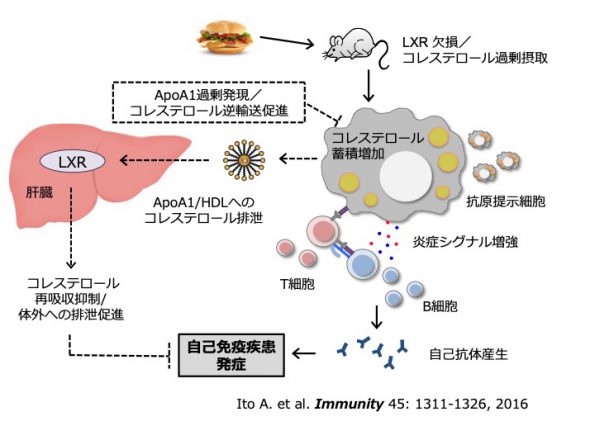
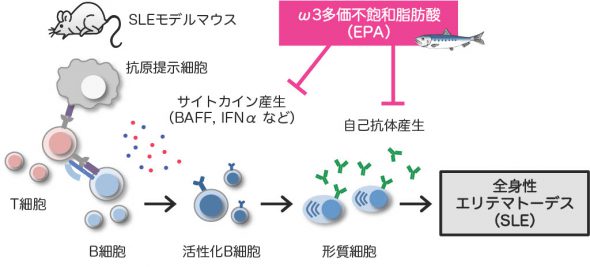
Accumulating evidence suggests that cholesterol accumulation in leukocytes is causally associated with the development of autoimmune diseases. However, the mechanism by which fatty acid composition influences autoimmune responses remains unclear. To determine whether the fatty acid composition of diet modulates leukocyte function and the development of systemic lupus erythematosus, we examined the effect of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) on the pathology of lupus in drug-induced and spontaneous mouse models. We found that dietary EPA supplementation ameliorated representative lupus manifestations, including autoantibody production and immunocomplex deposition in the kidneys. A combination of lipidomic and membrane dynamics analyses revealed that EPA remodels the lipid composition and fluidity of B cell membranes, thereby preventing B cell differentiation into autoantibody-producing plasma cells. These results highlight a previously unrecognized mechanism by which fatty acid composition affects B cell differentiation into autoantibody-producing plasma cells during autoimmunity, and imply that EPA supplementation may be beneficial for therapy of lupus.
Kobayashi A, et al. (2021) Dietary supplementation with eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits plasma cell differentiation and attenuates lupus autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 12:650856. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.650856
Biology & Life sciences